 Image 1 of 3
Image 1 of 3

 Image 2 of 3
Image 2 of 3

 Image 3 of 3
Image 3 of 3




Ethyl Maltol
Premium Synthetic Ingredient for Perfumery
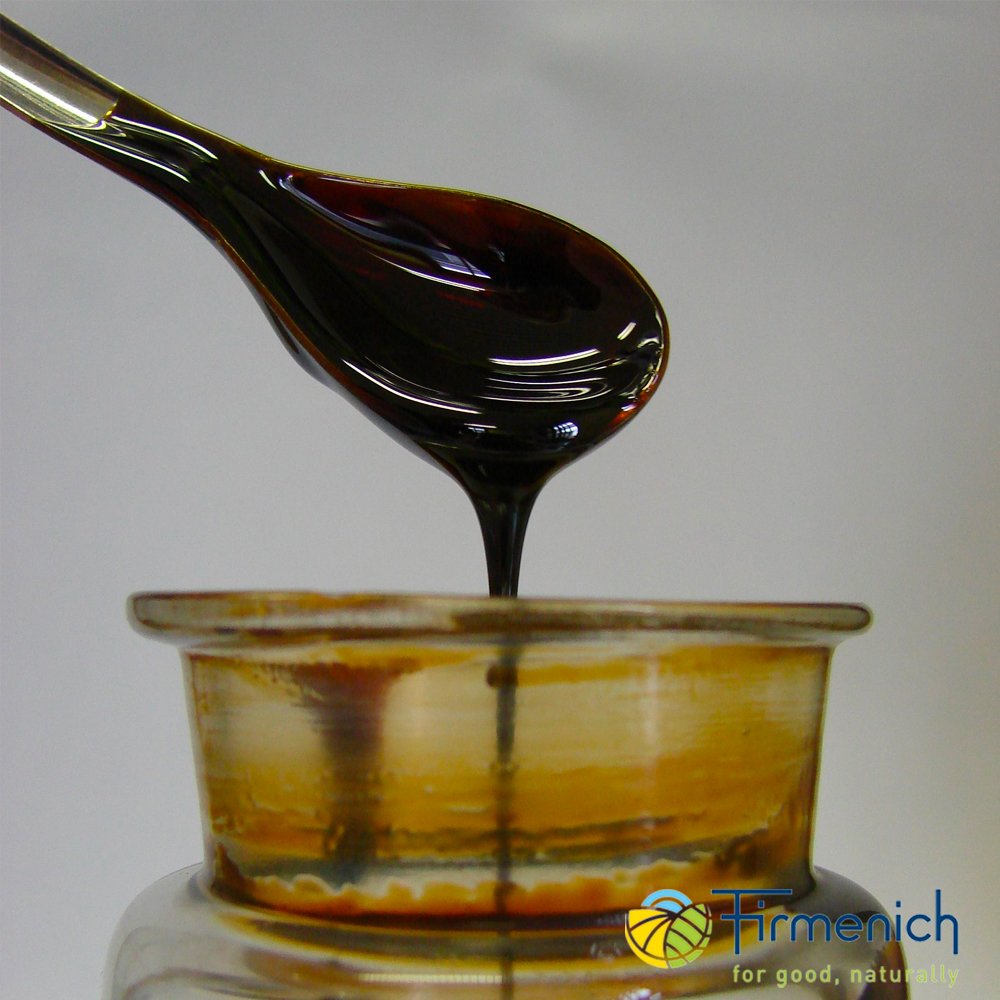
Ethyl Maltol (CAS 4940-11-8) is a synthetic perfumery ingredient known for its intensely sweet, caramellic, and jammy aroma reminiscent of candyfloss and fruit preserves. With a significantly higher potency than maltol—four to six times stronger—it is widely used to impart warmth and sweetness to gourmand, fruity, and vanilla-based compositions.
Its strong diffusion and high odor tenacity make it a key modifier in both perfumery and flavor applications, especially in enhancing edible or nostalgic scent profiles.
Premium Synthetic Ingredient for Perfumery
Ethyl Maltol (CAS 4940-11-8) is a synthetic perfumery ingredient known for its intensely sweet, caramellic, and jammy aroma reminiscent of candyfloss and fruit preserves. With a significantly higher potency than maltol—four to six times stronger—it is widely used to impart warmth and sweetness to gourmand, fruity, and vanilla-based compositions.
Its strong diffusion and high odor tenacity make it a key modifier in both perfumery and flavor applications, especially in enhancing edible or nostalgic scent profiles.
Premium Synthetic Ingredient for Perfumery
Ethyl Maltol (CAS 4940-11-8) is a synthetic perfumery ingredient known for its intensely sweet, caramellic, and jammy aroma reminiscent of candyfloss and fruit preserves. With a significantly higher potency than maltol—four to six times stronger—it is widely used to impart warmth and sweetness to gourmand, fruity, and vanilla-based compositions.
Its strong diffusion and high odor tenacity make it a key modifier in both perfumery and flavor applications, especially in enhancing edible or nostalgic scent profiles.
Technical Ingredient Overview
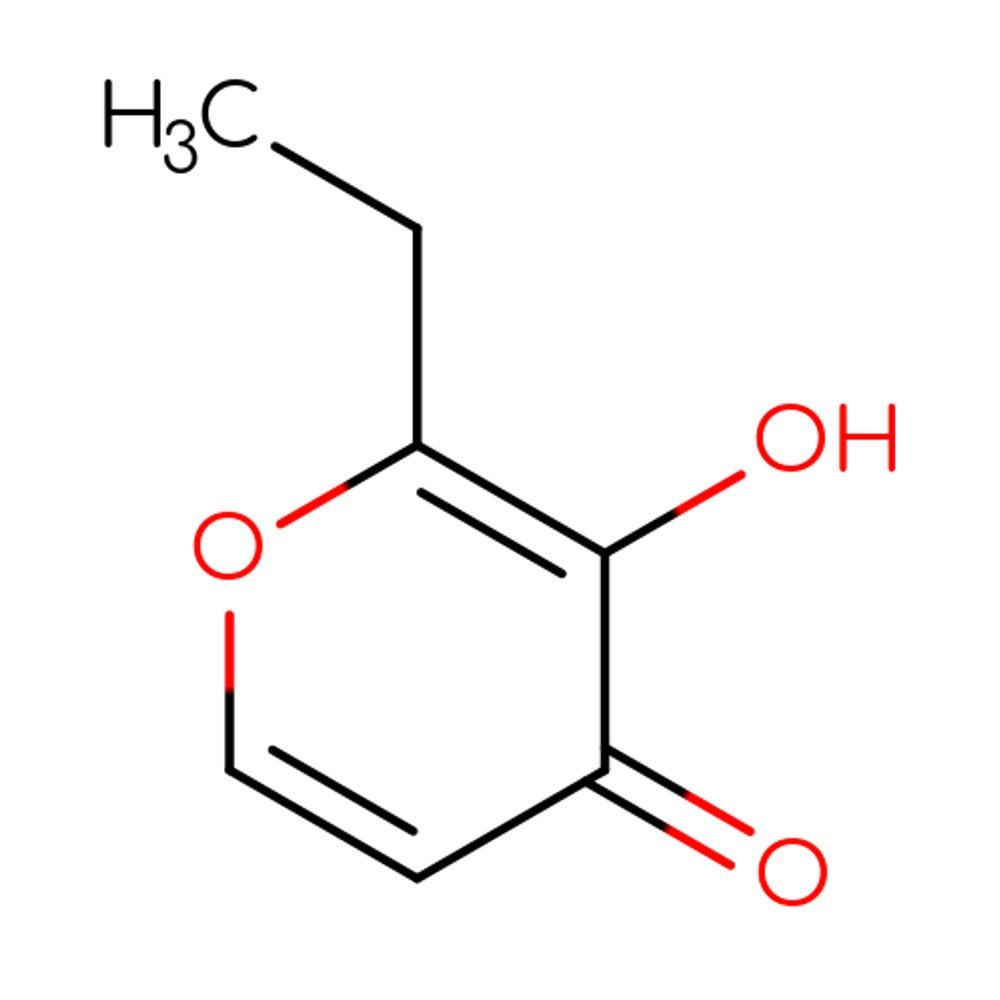
🔎 Chemical Name — Ethyl maltol
🧪 Synonyms — 2-Ethyl-3-hydroxy-4-pyrone
🧬 Chemical Formula — C₇H₈O₃
📂 CAS — 4940-11-8
📘 FEMA — 3487
⚖️ Molecular Weight (MW) — 140.14 g/mol
📝 Odor Type — Sweet → Gourmand (Caramellic)
📈 Odor Strength — Medium
👃🏼 Odor Profile — It has a sweet sugary, caramelised, jammy, strawberry-like odour reminiscent of candyfloss.
👅 Flavor Profile — Sweet, burnt cotton sugar candy like, with jammy, strawberry notes (Mosciano, Gerard P&F 16, No. 1, 31, (1991))
⚗️ Uses — It is a very powerful ingredient normally used at high dilution for sweetening blends or in conjunction with vanilla notes to create a rich, edible scent.
🧴 Appearance — White crystalline powder
What is Ethyl Maltol?
Ethyl Maltol is a high-impact aromatic compound used widely across perfumery and flavor industries. A derivative of maltol, this molecule offers a distinctly caramelized, jam-like sweetness that has become a cornerstone of modern gourmand fragrance design. Its ethyl substitution increases both volatility and olfactory strength, allowing it to act as both a central note and a diffusive enhancer in sweet or fruity accords.
Historical Background
Although today Ethyl Maltol is widely recognized for its role in gourmand perfumery and food flavoring, its history traces a rich intersection between natural chemistry and 20th-century industrial synthesis.
The molecule’s precursor, maltol (3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-pyrone), was first discovered in the early 20th century, naturally occurring in roasted malt, larch bark, and the thermal degradation products of carbohydrates. Maltol was formally described in early food chemistry literature as contributing to the crust-like, caramelized aroma of freshly baked goods (Arctander, 1960).
The synthesis of Ethyl Maltol—2-ethyl-3-hydroxy-4-pyrone—was achieved in the mid-to-late 20th century, likely by industrial chemists seeking more potent flavoring agents. The ethyl substitution on the pyrone ring confers significantly greater olfactory strength and thermal stability compared to maltol, making it ideal for high-temperature applications such as baking or perfume compounding.
A key milestone in the molecule’s development was the patent filed in 1969 by Charles R. Stephens Jr. and Robert P. Allingham for Pfizer Inc., describing the preparation and applications of Ethyl Maltol in flavor and fragrance compositions (U.S. Patent No. 3,585,263).
During the 1980s and 1990s, production scaled globally, with major expansion in China, where companies such as Zhaoqing Perfumery Co., Ltd. became leading suppliers. Today, several manufacturers report industrial production capacities exceeding 1,000 metric tons per year, primarily for use in food and tobacco flavoring, but also in perfumery.
In fragrance creation, Ethyl Maltol’s moment of innovation arrived with the launch of Angel (1992) by Mugler, composed by Olivier Cresp for Clarins. This fragrance marked a stylistic rupture: its overdose of caramelized, jammy, and candyfloss notes (partially derived from Ethyl Maltol) helped define the gourmand olfactory family, ushering in an era of perfumery grounded in edible nostalgia and fantasy.
Since then, Ethyl Maltol has remained a defining material of postmodern scent design, often used not only for its sweetness, but as a tool of emotional evocation—recalling childhood treats, red fruits, and festive indulgence.
Olfactory Profile
Scent Family: Gourmand
Descriptors: Cotton candy, caramel, jammy strawberry, toasted sugar
Intensity: Medium to strong
Tenacity: Excellent (long-lasting)
Volatility: Low to moderate
Fixative Role: Bridges fruity and vanillic materials, extends sweetness
Applications in Fine Fragrance
Ethyl Maltol is crucial in:
Gourmand compositions (chocolate, toffee, berry)
Fruity accords (enhancing strawberry, cherry, raspberry)
Oriental and amber structures for warmth and diffusion
Notable Synergies:
Vanillin: Reinforces creamy sweetness
Methyl Anthranilate: Adds grape-candy freshness
Gamma-Undecalactone: Evokes peach or milky fruit
Benzyl Acetate: Balances with floral-fruity brightness
Delta-Decalactone: Deepens creamy and coconut-like effects
Coumarin: Enhances ambery depth in sweet blends
Performance in Formula
Highly diffusive and bloom-enhancing at low concentrations (0.05–0.3%)
Acts as a rounder and smoother in fruity-lactonic blends
Stable in alcohol and oil bases; good thermal resistance
Ideal for bridging top-fruity and base-vanillic elements
Industrial & Technical Uses
Beyond perfumery, Ethyl Maltol is used in:
Confectionery and baked goods
Soft drinks and liqueurs
Tobacco and vaping liquids
Flavored cosmetics (e.g., lip balms)
It is prized for its low odor threshold and caramelic profile, making it one of the most effective sweet modifiers in food-grade and fragrance applications.
Key Patents and Industrial Development
Pfizer Inc.
Ethyl Maltol was formally patented in 1969 by Charles R. Stephens Jr. and Robert P. Allingham, researchers at Pfizer Inc. The patent (U.S. Patent No. 3,585,263, granted in 1971) outlined the synthesis of 2-ethyl-3-hydroxy-4-pyrone and its use as a flavor and fragrance agent. This marked the compound's first official entry into the industrial domain and paved the way for its approval in both the food and cosmetics sectors.
Givaudan S.A.
The Swiss fragrance house Givaudan has incorporated Ethyl Maltol in numerous proprietary perfume compositions. While not the originator of the molecule, Givaudan’s use of Ethyl Maltol in modern gourmand accords is well documented through their published patents and fragrance creations, reinforcing its importance as a creative tool in fine perfumery.
Zhaoqing Perfumery Co., Ltd.
Based in Guangdong, China, Zhaoqing Perfumery Co. emerged in the 1980s as one of the first companies to produce Ethyl Maltol at industrial scale in the Asian market. The company is currently among the world’s leading suppliers, with an annual production capacity reportedly exceeding 1,000 metric tons, supplying raw materials to the global flavor and fragrance industry.
Regulatory & Safety Overview
IFRA Status: Not restricted (as of IFRA 51st Amendment)
FEMA: 3487 (GRAS listed)
EU Cosmetics Regulation: Not restricted in Annexes II–V
GHS Classification: Not hazardous under normal use
REACH: Registered; not considered a SVHC
Toxicology:
Oral LD₅₀ (rat): >1000 mg/kg
No notable dermal or respiratory risks under typical usage
References
Arctander, S. (1960). Perfume and Flavor Chemicals (Aroma Chemicals).
Sell, C. (2006). The Chemistry of Fragrances (2nd ed.). RSC Publishing.
JECFA (1999). Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants.
IFRA. (2023). Standards Library – Amendment 51.
PubChem (n.d.). Ethyl Maltol. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/7789
European Commission (2009). Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 on Cosmetic Products.
Arctander, S. (1960). Perfume and Flavor Chemicals (Aroma Chemicals). Montclair, NJ: Allured Publishing.
Sell, C. (2006). The Chemistry of Fragrances: From Perfumer to Consumer (2nd ed.). Cambridge: RSC Publishing.
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. (1999). Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants. WHO Technical Report Series.
IFRA. (2023). IFRA Standards Library – 51st Amendment.
PubChem. (n.d.). Ethyl Maltol. National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/7789
U.S. Patent No. 3,585,263. (1971). Preparation and Use of Ethyl Maltol. Inventors: Stephens, C. R., & Allingham, R. P. Assignee: Pfizer Inc.
[Zhaoqing Perfumery Co., Ltd.]. (n.d.). Technical Data Sheet: Ethyl Maltol.