 Image 1 of 2
Image 1 of 2

 Image 2 of 2
Image 2 of 2



Acetophenone
Premium Synthetic Ingredient for Perfumery
Acetophenone (CAS 98-86-2) is a synthetic aromatic ketone, industrially derived as a by-product of ethylbenzene oxidation—a key process in styrene production. While primarily synthetic, it occurs in trace amounts in plants and animal secretions such as castoreum. Its molecular simplicity and reactivity make it a benchmark material in carbonyl chemistry and organic synthesis.
In perfumery, acetophenone is valued for its powdery, heliotrope-like facets and fixative contribution. Its olfactory profile blends almond-like sweetness with subtle floral depth, lending body and narcotic warmth to cherry, heliotrope, and vintage floral accords.
Premium Synthetic Ingredient for Perfumery
Acetophenone (CAS 98-86-2) is a synthetic aromatic ketone, industrially derived as a by-product of ethylbenzene oxidation—a key process in styrene production. While primarily synthetic, it occurs in trace amounts in plants and animal secretions such as castoreum. Its molecular simplicity and reactivity make it a benchmark material in carbonyl chemistry and organic synthesis.
In perfumery, acetophenone is valued for its powdery, heliotrope-like facets and fixative contribution. Its olfactory profile blends almond-like sweetness with subtle floral depth, lending body and narcotic warmth to cherry, heliotrope, and vintage floral accords.
Premium Synthetic Ingredient for Perfumery
Acetophenone (CAS 98-86-2) is a synthetic aromatic ketone, industrially derived as a by-product of ethylbenzene oxidation—a key process in styrene production. While primarily synthetic, it occurs in trace amounts in plants and animal secretions such as castoreum. Its molecular simplicity and reactivity make it a benchmark material in carbonyl chemistry and organic synthesis.
In perfumery, acetophenone is valued for its powdery, heliotrope-like facets and fixative contribution. Its olfactory profile blends almond-like sweetness with subtle floral depth, lending body and narcotic warmth to cherry, heliotrope, and vintage floral accords.
tecnical Ingredient Overview
🏭 Manufacturer: (Not specified)
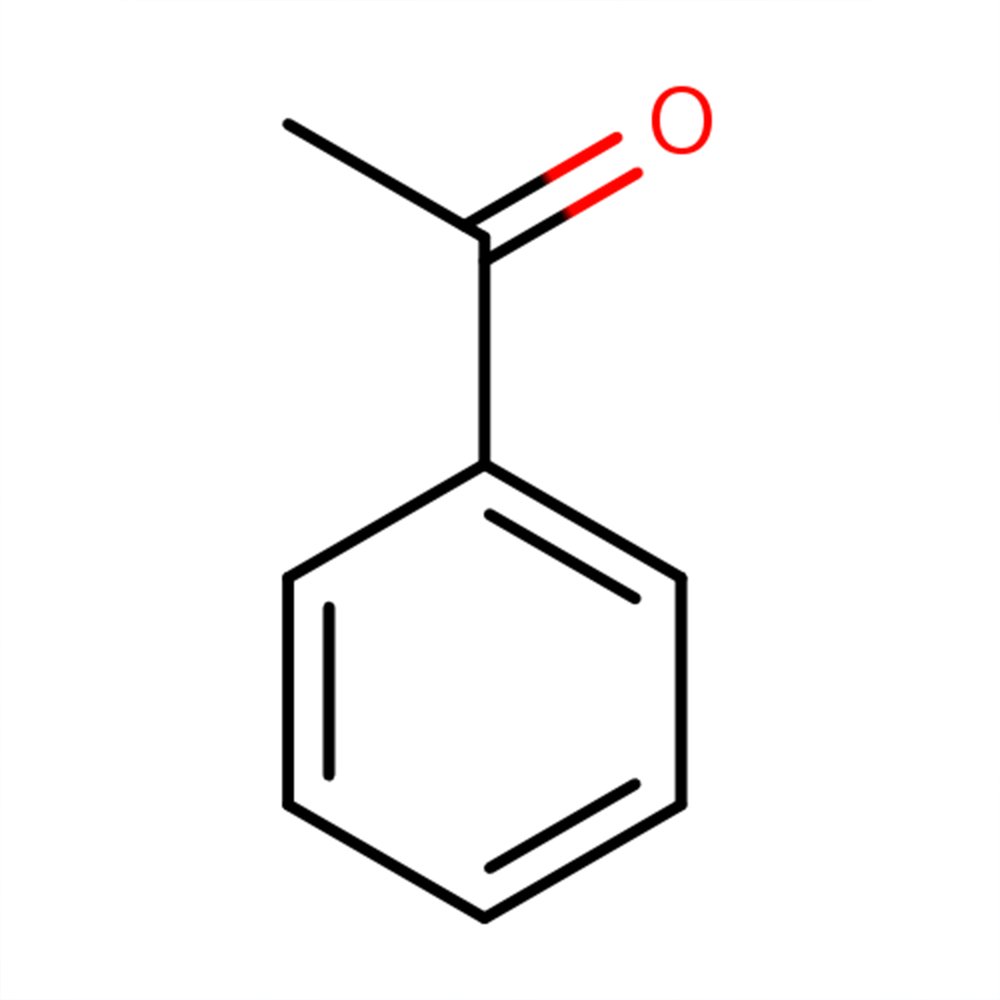
🔎 Chemical Name: Acetophenone
🧪 Synonyms: 1-Phenylethanone, Methyl phenyl ketone, Phenyl methyl ketone
🧬 Chemical Formula: C₈H₈O
📂 CAS N°: 98-86-2
📘 FEMA: 2009
⚖️ MW: 120.15 g/mol
📝 Odor Type: Sweet, Balsamic
📈 Odor Strength: Medium to Strong
👃🏼 Odor Profile: Sweet, almond-like, balsamic, floral nuances (reminiscent of hawthorn and narcissus)
⚗️ Uses: Fine fragrance, flavoring agent, solvent, fixative component
🧴 Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow liquid
What is Acetophenone?
Acetophenone is a simple aromatic ketone characterized by a phenyl ring attached to a carbonyl group. Structurally, it is the simplest ketone derivative of acetophenyl compounds and is naturally present in trace amounts in various foods and essential oils, such as acacia, black tea, and apple. In perfumery, it is known for its distinctive sweet, floral-balsamic scent and is widely used for its fixative properties and role in florals, especially hawthorn and almond notes.
Historical Background
Acetophenone was first synthesized in the 19th century and gained attention for both its industrial potential and sensory properties. Early references to its synthesis date back to Friedel-Crafts acylation processes, a foundational method in organic chemistry. Historically, acetophenone was one of the first aromatic ketones to be industrially produced and was once used pharmaceutically as a hypnotic under the trade name Hypnone (Sell, 2014).
Its use in perfumery developed in the early 20th century, particularly in the recreation of hawthorn accords and mimosa effects. Over time, it became a key building block in both fragrance design and synthetic organic chemistry.
Olfactory Profile
Acetophenone belongs to the sweet balsamic olfactory family, presenting a rich bouquet of almond-like, slightly floral, and powdery nuances. It is particularly valuable for hawthorn, mimosa, and orange blossom reconstructions. While it does not possess high tenacity on its own, it blends effectively with ionones, heliotropin, anisic aldehyde, and benzyl acetate.
Applications in Fine Fragrance
In perfumery, Acetophenone is primarily used:
As a modifier and accentuator in floral compositions.
In mimosa, narcissus, and hawthorn accords.
To add a powdery, slightly animalic tone when combined with musks or heliotropin.
It is present in several historical formulations and continues to be used in retro-style perfumes, as well as in flavorings due to its sweet and slightly fruity edge.
Performance in Formula
Diffusion: Moderate, especially in top-to-heart transition.
Fixative Strength: Mild to moderate.
Stability: Stable in most media; may yellow slightly over time.
Compatibility: Blends well with esters, aldehydes, lactones, and ionones.
Industrial & Technical Uses
Beyond perfumery, acetophenone is used:
As a precursor in organic synthesis (e.g., for pharmaceuticals like amphetamines and resins).
As a solvent for plastics and resins.
In flavor applications, where it imparts cherry, almond, and floral notes (FEMA GRAS listing #2009).
Formerly used in sedative formulations, although this application is now obsolete.
Regulatory & Safety Overview
IFRA Status: Not restricted under the current IFRA 51st Amendment. Safe within typical usage levels for fragrance and flavor applications.
GHS Classification:
Signal Word: Warning
Hazards: H319 (Causes serious eye irritation), H302 (Harmful if swallowed), H332 (Harmful if inhaled)
EU Cosmetics Regulation: Permitted; usage levels must comply with safety assessments.
REACH: Registered; no specific restriction when used within limits.
Allergen Risk: Not classified as a fragrance allergen per Annex III of the EU Cosmetics Regulation.
FEMA: Approved for food flavoring with GRAS status (FEMA #2009).
Toxicology: Acute exposure may cause irritation; high doses have CNS depressant effects (Sell, 2014; PubChem, 2024).
References
Arctander, S. (1960). Perfume and Flavor Chemicals (Aroma Chemicals). Montclair: Author.
Sell, C. S. (2014). The Chemistry of Fragrances: From Perfumer to Consumer (2nd ed.). Royal Society of Chemistry.
Surburg, H., & Panten, J. (2016). Common Fragrance and Flavor Materials: Preparation, Properties and Uses (6th ed.). Wiley-VCH.
PubChem. (2024). Acetophenone — CID 7410. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Acetophenone
FEMA (2023). Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association — FEMA Number 2009. Retrieved from https://www.femaflavor.org/