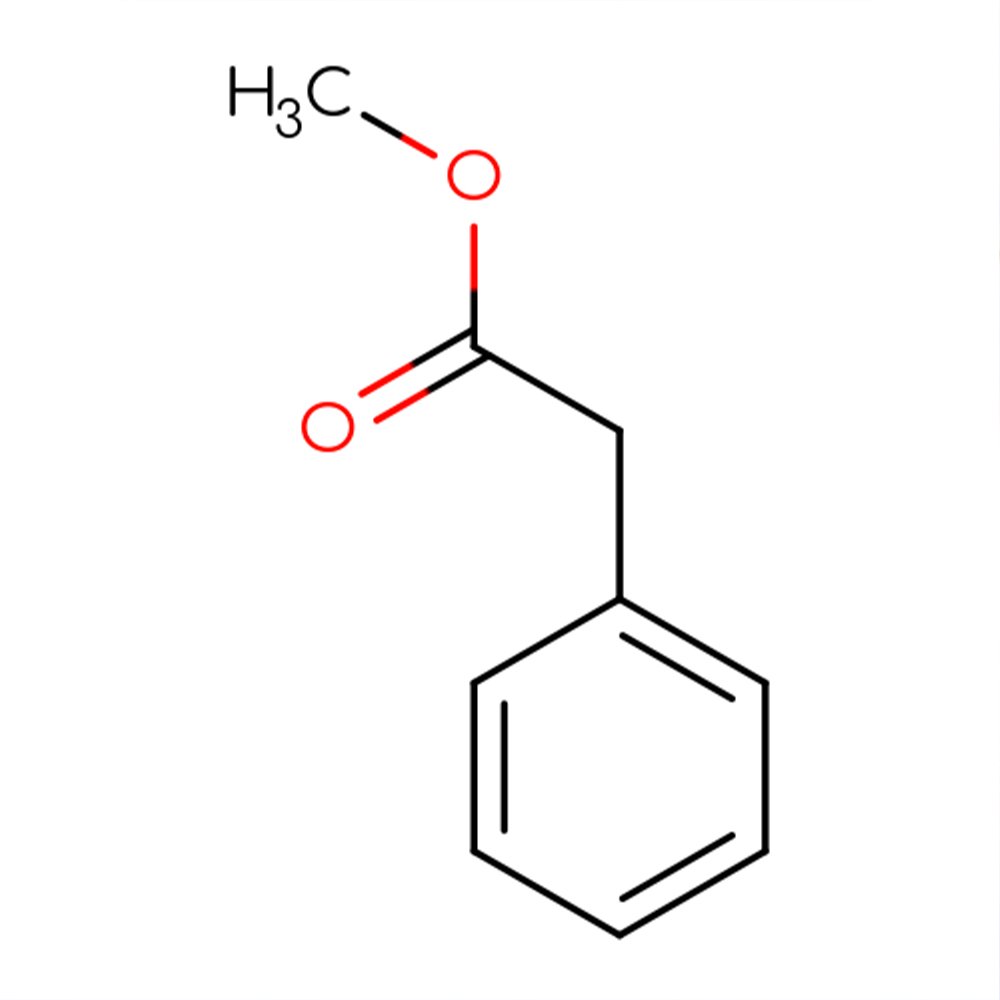
Methyl Phenylacetate Technical Ingredient Overview
🔎 Chemical Name — Methyl 2-phenylacetate
🧪 Synonyms — Phenylacetic acid methyl ester; Benzeneacetic acid methyl ester; Methyl benzylformate; Methyl alpha-toluate
📂 CAS Number — 101-41-7
📘 FEMA Number — 2733
⚖️ Molecular Weight — 150.17 g/mol
📝 Odor Type — Floral-honey
📈 Odor Strength — Very high intensity; powerful and diffusive
👃🏼 Odor Profile — Intensely sweet honey-floral with jasmine-musky nuances, waxy-spicy undertones, evolving into fruity-almond facets with tenacious animalic drydown
⚗️ Uses — Fine fragrance modifier, functional perfumery, flavor ingredient, solvent masking agent
🧴 Appearance — Colorless to pale yellow liquid
What is Methyl Phenylacetate?
Methyl phenylacetate is a synthetic aromatic ester with the molecular formula C₉H₁₀O₂, formed through the esterification of phenylacetic acid with methanol. This compound belongs to the phenylacetate ester family and is classified as an aromatic ester within the broader category of benzyl derivatives (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, 2018).
The molecule consists of a benzyl group (C₆H₅CH₂-) attached to a carboxylate ester functional group (-COOCH₃), giving it the structural formula C₆H₅CH₂COOCH₃. As a clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid with limited water solubility but high solubility in alcohols and organic solvents, methyl phenylacetate exhibits excellent compatibility with standard perfumery carriers (TCI America, n.d.).
Despite being synthetically produced for commercial applications, methyl phenylacetate occurs naturally in trace quantities in honey, wine, coffee, cocoa, brandy, pepper, and various fermented products (Sigma-Aldrich, n.d.).
Historical Background
The industrial synthesis and application of methyl phenylacetate in perfumery dates to the early 20th century as part of the broader development of synthetic phenylacetic acid derivatives. The compound emerged during the expansion of synthetic aromatic chemistry when perfumers sought cost-effective alternatives to natural flower extracts.
Production methods evolved from early batch esterification processes to modern continuous synthesis via the hydrolysis of phenylacetonitrile (derived from benzyl chloride and sodium cyanide) followed by esterification with methanol under acidic conditions (Lookchem, n.d.). This synthetic route, utilizing benzyl cyanide as an intermediate, became the predominant industrial method due to efficiency and yield optimization.
By mid-century, methyl phenylacetate had become established as a standard component in jasmine and rose reconstitutions, particularly valued for its economic advantage and powerful diffusion characteristics.
Olfactory Profile
Scent Family
Floral-honey with secondary musky-animalic characteristics
Main Descriptors
Methyl phenylacetate presents an intensely sweet, honey-like floralcy as its primary olfactory characteristic. The opening impression is powerfully diffusive with bright honey-sweet notes that immediately dominate the olfactory space.
Secondary characteristics include:
Jasmine-musky nuances providing depth and sophistication
Waxy-spicy undertones adding textural complexity
Fruity-almond facets emerging in the heart phase
Tenacious animalic drydown with musky persistence
The compound exhibits what perfumers describe as a "unclean" or sharp animalic edge when used in high concentrations, necessitating careful dosage control (Scentspiracy, n.d.).
Intensity
Very high to extreme. The odor strength is exceptionally powerful and diffusive, with the compound detectable at very low concentrations. Industry practice recommends evaluation at 10% dilution or lower due to its overwhelming intensity at full strength (Home Sunshine Pharma, n.d.).
Tenacity
High tenacity with persistence exceeding 48 hours on smelling strips. The material exhibits strong substantivity on both paper and fabric substrates.
Volatility
Top-to-heart note classification. While initially presenting as a bright, diffusive top note, the compound's molecular weight (150.17 g/mol) and substantivity place it functionally in the top-to-heart transition zone with extended persistence into the middle phase.
Applications in Fine Fragrance
Methyl phenylacetate functions primarily as a high-impact floral modifier and sweetening agent in perfume compositions. Its role is typically supportive rather than dominant, used to enhance and sweeten existing accords rather than define them.
Primary applications:
Rose compositions: Sweetening and enriching classic rose accords, particularly in rose eglantine variants
Jasmine bases: Adding honey-sweet depth and musky persistence to jasmine reconstructions
Oriental fragrances: Contributing waxy, honey-rich body to amber and vanilla structures
Tobacco accords: Providing sweet-floral contrast and complexity
Typical pairing behavior: Synergizes effectively with indole, phenylethyl alcohol, hydroxycitronellal, and aliphatic aldehydes. Shows particular affinity for rose oxide, geraniol, and floral musks.
Performance in Formula
Methyl phenylacetate demonstrates excellent solvent compatibility in alcohol-based systems with minimal water solubility (Sigma-Aldrich, n.d.). The compound requires controlled dosage—typically below 1% in fine fragrance and below 35 ppm in flavor applications—to prevent the emergence of sharp, unclean animalic notes.
Impact on composition: Acts as a potent sweetener and diffusion enhancer, capable of dramatically altering the character of a formula at low concentrations. Functions effectively as a solvent masking agent in functional applications.
Industrial & Technical Uses
Beyond perfumery, methyl phenylacetate serves as:
Flavor ingredient (FEMA GRAS 2733) for honey, chocolate, and tobacco flavoring
Organic synthesis intermediate in pharmaceutical production (atropine, anisodamine synthesis)
Research reagent for partition coefficient studies and acylation reactions with penicillin G amidase (Sigma-Aldrich, n.d.)
Regulatory & Safety Overview
IFRA Status
No specific restrictions under IFRA Amendment 51 (notified June 30, 2023). The material is permitted for use across all fragrance categories without concentration limits, though formulators should adhere to good manufacturing practices (Scentspiracy, n.d.; Fraterworks, n.d.).
Reference: IFRA Standards Library - https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
EU Cosmetics Regulation
Compliant with EU Regulation 1223/2009. Not listed among the 26 mandatory declarable allergens. EINECS Number: 202-940-9 (ChemIDplus, n.d.).
FEMA Status
GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) under FEMA Number 2733 for use in food flavoring applications under specified concentration limits (Sigma-Aldrich, n.d.).
Toxicology
Oral LD50 in rats: approximately 599 mg/kg (moderate toxicity). The compound shows minimal skin irritation or sensitization potential under standard use conditions. Classified as combustible liquid; incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong bases (Home Sunshine Pharma, n.d.).
References
Api, A. M., et al. (2018). RIFM fragrance ingredient safety assessment, methyl phenylacetate, CAS Registry Number 101-41-7. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 122(Suppl 1), S453-S460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.09.053
ChemIDplus. (n.d.). Methyl phenylacetate. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved October 2025, from https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/sid/0000101417
Fengchen Group. (n.d.). Methyl phenylacetate or methyl phenyl acetate CAS 101-41-7. Retrieved October 2025, from https://www.fengchengroup.com/chemicals/featured-chemicals/methyl-phenylacetate-or-methyl-phenyl-acetate.html
Home Sunshine Pharma. (n.d.). Methyl phenylacetate CAS 101-41-7. Retrieved October 2025, from https://www.hsppharma.com/apis-and-intermediates/methyl-phenylacetate-cas-101-41-7.html
IFRA. (2023). Notification of the 51st Amendment to the IFRA Standards. International Fragrance Association. https://ifrafragrance.org/docs/default-source/51st-amendment/ifra-standards---51st-amendment.pdf
Lookchem. (n.d.). Cas 101-41-7, Methyl phenylacetate. Retrieved October 2025, from https://www.lookchem.com/casno101-41-7.html
PubChem. (n.d.). Methyl phenylacetate. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved October 2025, from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/101-41-7
Santa Cruz Biotechnology. (2018). Methyl phenylacetate CAS 101-41-7. Retrieved October 2025, from https://www.scbt.com/p/methyl-phenylacetate-101-41-7
Sigma-Aldrich. (n.d.). Methyl phenylacetate ≥98%, FCC, FG. Retrieved October 2025, from https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/product/aldrich/w273309
TCI America. (n.d.). Methyl phenylacetate. Retrieved October 2025, from https://www.tcichemicals.com/US/en/p/P0125