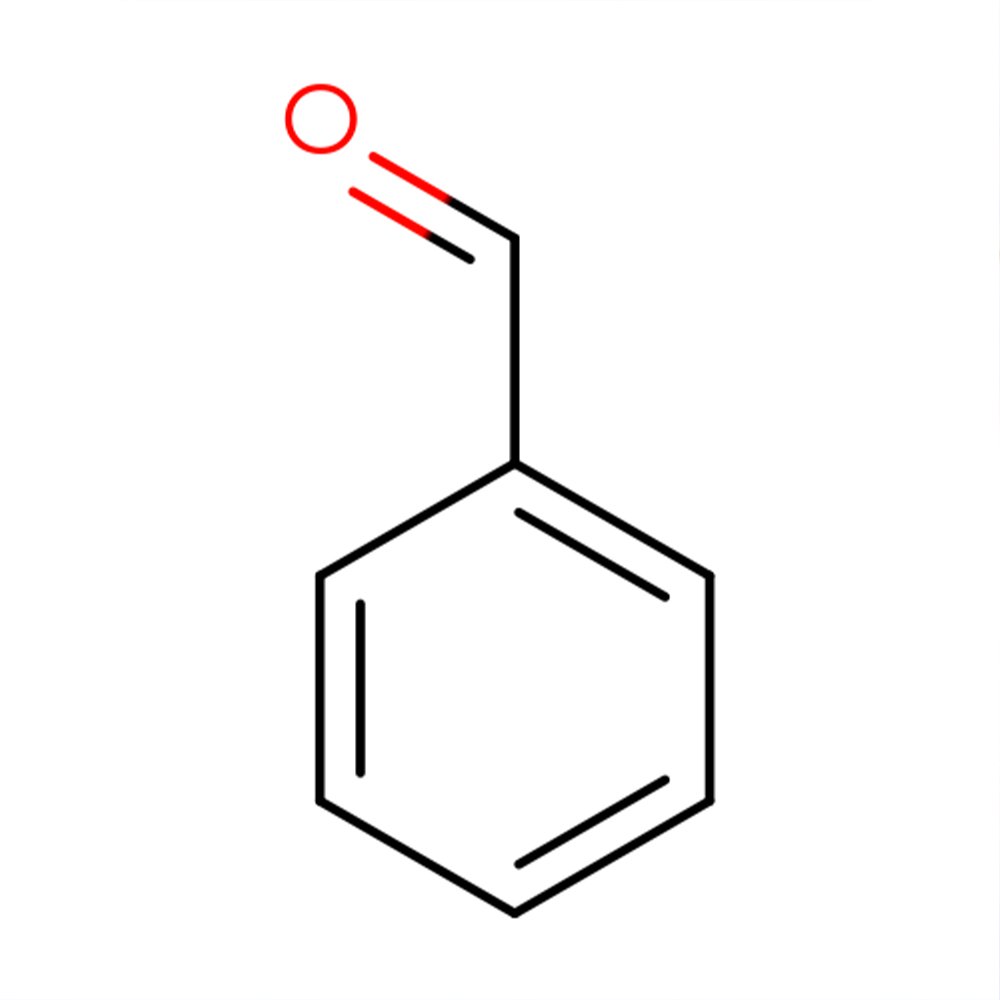
Benzoic Aldehyde
Premium Natural-Derived Ingredient for Perfumery
Benzaldehyde is a naturally occurring aromatic aldehyde known for its intense bitter almond note. First identified in bitter almond oil, it is now primarily produced via synthetic oxidation of toluene. Volatile and sharp, it plays a key role in the fruity-almond and cherry facets of perfumery and flavor design.
Used as a top-note modifier or trace component in floral compositions, its dual olfactory and flavor function makes it a versatile raw material in both perfumery and industrial synthesis.
Premium Natural-Derived Ingredient for Perfumery
Benzaldehyde is a naturally occurring aromatic aldehyde known for its intense bitter almond note. First identified in bitter almond oil, it is now primarily produced via synthetic oxidation of toluene. Volatile and sharp, it plays a key role in the fruity-almond and cherry facets of perfumery and flavor design.
Used as a top-note modifier or trace component in floral compositions, its dual olfactory and flavor function makes it a versatile raw material in both perfumery and industrial synthesis.
Premium Natural-Derived Ingredient for Perfumery
Benzaldehyde is a naturally occurring aromatic aldehyde known for its intense bitter almond note. First identified in bitter almond oil, it is now primarily produced via synthetic oxidation of toluene. Volatile and sharp, it plays a key role in the fruity-almond and cherry facets of perfumery and flavor design.
Used as a top-note modifier or trace component in floral compositions, its dual olfactory and flavor function makes it a versatile raw material in both perfumery and industrial synthesis.
technical Ingredient Overview
🔎 Chemical Name — Benzaldehyde
🧪 Synonyms — Benzenecarbaldehyde, Phenylmethanal, Artificial almond oil
🧬 Chemical Formula — C₇H₆O
📂 CAS — 100-52-7
📘 FEMA — 2127
⚖️ MW — 106.12 g/mol
📝 Odor Type — Aromatic aldehyde
📈 Odor Strength — Strong
👃🏼 Odor Profile — Sweet, almond-like, cherry nuances
⚗️ Uses — Fragrance component, flavoring agent, intermediate
🧴 Appearance — Colorless to pale yellow liquid
What is Benzaldehyde?
Benzaldehyde is the simplest aromatic aldehyde, consisting of a benzene ring substituted with a formyl group. Naturally present in bitter almond oil, apricot kernels, and other stone fruits, it is widely used in perfumery and flavoring for its distinctive almond-cherry aroma. As a member of the aromatic aldehydes family, it serves as a foundational compound in both olfactory design and synthetic organic chemistry (Sell, 2006; Arctander, 1960).
Historical Background
Benzaldehyde was formally identified in 1832 by two foundational figures in organic chemistry, Friedrich Wöhler and Justus von Liebig, through their investigation of bitter almond oil (Prunus amygdalus var. amara). In their seminal paper, Untersuchungen über das Radikal der Benzoesäure, they described the compound responsible for the characteristic scent of almonds and introduced one of the first functional group concepts applied to aromatic molecules (Wöhler & Liebig, 1832).
Although benzoic acid had been known since the 16th century (isolated from gum benzoin), Wöhler and Liebig’s work on benzaldehyde marked a decisive turn toward a more rational, structural understanding of organic compounds. The oxidation pathway from benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde to benzoic acid became a cornerstone example in the pedagogy of redox chemistry (Kraft, 2006).
Benzaldehyde’s minimal yet functionally rich structure — a benzene ring bearing an aldehyde group — made it a central molecule in 19th-century discussions around aromatic substitution and reactivity. It effectively bridged the empirical traditions of natural product isolation with the emerging science of organic synthesis.
In later decades, its intense, sweet aroma and recognizable top note character positioned it as an early precursor to the rise of aldehydes in perfumery, ultimately inspiring generations of synthetic aromachemicals that shaped 20th-century fragrance design.
Olfactory Profile
Family: Aromatic aldehydes
Descriptors: Sweet, almond, cherry, marzipan-like, slightly fruity
Intensity: Strong
Tenacity: Low (volatile)
Applications in Fine Fragrance
Benzaldehyde is a staple material for floral and gourmand accords, particularly in compositions mimicking lilac, heliotrope, and violet. It is frequently paired with Heliotropex to create creamy, sweet floral blends, or used in almond and pastry-like accords alongside vanillin and coumarin (Arctander, 1960).
Performance in Formula
Functioning as a powerful top note, benzaldehyde brings brightness and immediacy to a composition but requires reinforcement due to its volatility. It synergizes well with Alpha-Ionone in floral contexts and with anisic or balsamic notes in gourmand constructions. Fixation can be improved by anchoring it to long-lasting sweet or lactonic materials.
Industrial & Technical Uses
Beyond perfumery, benzaldehyde is an important intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyes (notably aurin and malachite green), cinnamic acid derivatives, and resins. It is also used industrially as a solvent and in agrochemical formulations (Sell, 2006).
Regulatory & Safety Overview
IFRA 51st Amendment:
Category 4 (Fine Fragrance): Max 0.27%
Category 5 (Leave-on Skin): Max 0.14%
FEMA GRAS: No. 2127
REACH: Registered; not PBT or vPvB
ECHA: Classified as irritant; potential skin sensitizer
JECFA: Flavoring agent, evaluated as compound No. 22
While generally regarded as safe in low concentrations, benzaldehyde should be dosed conservatively in skin-contact formulations due to potential sensitization. Always review full IFRA guidance before inclusion in fragrance design (IFRA, 2023; FEMA, 2024; ECHA, 2024).
Internal Links Summary
References
Arctander, S. (1960). Perfume and Flavor Chemicals (Aroma Chemicals). Montclair: Self-Published.
ECHA. (2024). Benzaldehyde (CAS 100-52-7) dossier. Retrieved from https://echa.europa.eu
FEMA. (2024). Flavor Ingredient Library: Benzaldehyde (FEMA 2127). Retrieved from https://www.femaflavor.org
IFRA. (2023). IFRA Standards, 51st Amendment. Retrieved from https://ifrafragrance.org
Kraft, P. (2006). Aroma chemicals and the language of smell. Chimia, 60(3), 111–118.
Sell, C. S. (2006). The Chemistry of Fragrances (2nd ed.). Royal Society of Chemistry.
Wöhler, F., & Liebig, J. (1832). Untersuchungen über das Radikal der Benzoesäure. Annalen der Pharmacie, 3(3), 249–282.