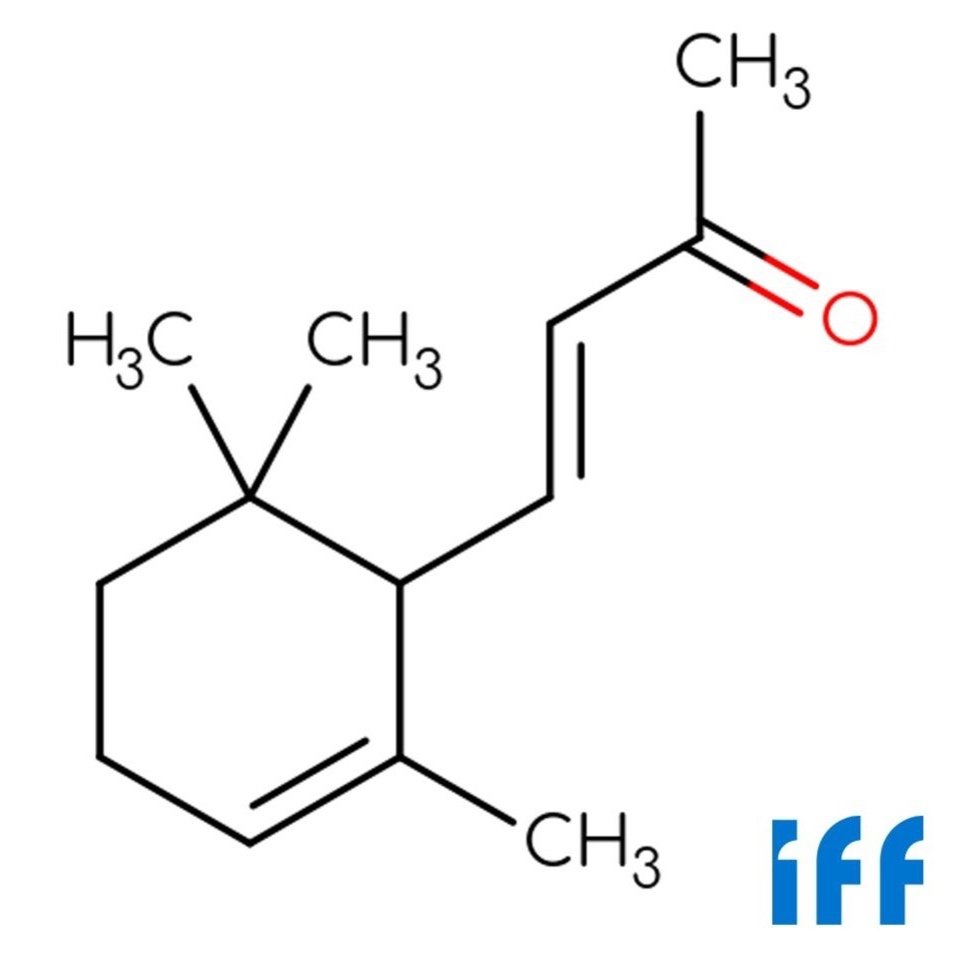
 Image 1 of 3
Image 1 of 3

 Image 2 of 3
Image 2 of 3

 Image 3 of 3
Image 3 of 3




Alpha Ionone (Toco)
Premium Synthetic Ingredient for Perfumery
Alpha-Ionone (CAS 127-41-3) is a synthetic ketone compound known for its elegant violet-like aroma, with soft woody and balsamic undertones. First synthesized in 1893 from citral and acetone, it remains one of the most historically important aroma materials in perfumery.
Alpha-Ionone's distinctive scent profile—powdery, floral, and mildly fruity—has made it a core component in rose bases, violet accords, and various floral-woody compositions.Produced today by IFF, it continues to serve as a key material in both fine fragrance and flavor formulations.
Premium Synthetic Ingredient for Perfumery
Alpha-Ionone (CAS 127-41-3) is a synthetic ketone compound known for its elegant violet-like aroma, with soft woody and balsamic undertones. First synthesized in 1893 from citral and acetone, it remains one of the most historically important aroma materials in perfumery.
Alpha-Ionone's distinctive scent profile—powdery, floral, and mildly fruity—has made it a core component in rose bases, violet accords, and various floral-woody compositions.Produced today by IFF, it continues to serve as a key material in both fine fragrance and flavor formulations.
Premium Synthetic Ingredient for Perfumery
Alpha-Ionone (CAS 127-41-3) is a synthetic ketone compound known for its elegant violet-like aroma, with soft woody and balsamic undertones. First synthesized in 1893 from citral and acetone, it remains one of the most historically important aroma materials in perfumery.
Alpha-Ionone's distinctive scent profile—powdery, floral, and mildly fruity—has made it a core component in rose bases, violet accords, and various floral-woody compositions.Produced today by IFF, it continues to serve as a key material in both fine fragrance and flavor formulations.
Technical Ingredient Overview
🔎 Chemical Name — Alpha-Ionone
🧪 Synonyms — α-Ionone; 4-(2,6,6-Trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-3-buten-2-one
🧬 Chemical Formula — C₁₃H₂₀O
📂 CAS — 127-41-3
📘 FEMA — 2594
⚖️ MW — 192.30 g/mol
📝 Odor Type — Floral, Woody
📈 Odor Strength — Medium
👃🏼 Odor Profile — Powdery violet, floral, woody, berry, slightly fruity, warm
⚗️ Uses — Fine fragrance, cosmetics, functional perfumery, flavoring agent (FEMA GRAS)
🧴 Appearance — Colorless to pale yellow liquid
What is Alpha-Ionone?
Alpha-Ionone is a monocyclic terpene ketone within the ionone family, structurally derived from the oxidative degradation of carotenoids such as β-carotene (Surburg & Panten, 2016). It plays a crucial role in perfumery and flavoring due to its warm, floral-fruity aroma reminiscent of violet and raspberry notes. Although it occurs in trace amounts in certain natural sources, its commercial form is predominantly synthetic (Arctander, 1960).
Historical Background
Alpha-Ionone was first characterized in the late 19th century during investigations into the breakdown of carotenoids. German chemists Wilhelm Haarmann and Ferdinand Tiemann were instrumental in its early development around 1893, as they sought to reproduce the elusive scent of violets synthetically (Sell, 2006). The synthesis of α-ionone and its isomers revolutionized perfumery by enabling the creation of violet-scented fragrances at scale, most notably in Après l’Ondée by Guerlain (Arctander, 1960).
Olfactory Profile
Alpha-Ionone is part of the floral-woody olfactory family, known for its soft powdery floral character. It exhibits violet, orris, and berry nuances with a warm undertone, less woody and more floral compared to β-ionone (Surburg & Panten, 2016).
Odor intensity: Medium
Tenacity: Moderate to high (lasting several days on blotter)
Volatility: Medium
Fixative role: Acts both as a heart note and a mild fixative
Applications in Fine Fragrance
Alpha-Ionone is frequently used to:
Reconstruct violet and orris accords
Round off aldehydic or citrusy top notes
Support mimosa, osmanthus, and rose bouquets
It is especially valued for its ability to impart softness and volume to floral arrangements. It synergizes effectively with methyl ionone, damascones, and rose ketones (Sell, 2006).
Performance in Formula
It brings diffusion, roundness, and soft floral depth to a composition. Its moderate tenacity and compatibility with various musks, woods, and floral aromachemicals make it versatile in both feminine and unisex formulas (Arctander, 1960).
Industrial & Technical Uses
Aside from fine fragrance, alpha-ionone is used in:
Flavor formulations (FEMA 2594), especially for berry, raspberry, and floral-vanilla profiles
Cosmetic products, especially powders and skin creams, for its soft, clean violet note
Functional perfumery such as air care and laundry, providing a floral-powdery dimension (Surburg & Panten, 2016)
Regulatory & Safety Overview
IFRA Status: Not individually restricted in IFRA 51st Amendment (IFRA, 2023), but may be subject to concentration limits in specific classes due to combined use with other ionones.
GHS Classification: Not classified as hazardous under standard usage levels (European Commission, 2023).
EU Cosmetic Regulation: Allowed without specific restriction, not listed among 26 declarable allergens (CosIng, 2023).
FEMA Status: FEMA 2594; GRAS as a flavoring agent (FEMA, 2023).
Toxicology: Considered to have low acute toxicity and minimal sensitization potential (Opdyke, 1974).
REACH: Fully registered with safety dossier available for industrial use within the EU.
References
Arctander, S. (1960). Perfume and Flavor Chemicals (Aroma Chemicals). Montclair, NJ: Author.
European Commission. (2023). CosIng – Cosmetic Ingredients and Substances Database. Retrieved from https://ec.europa.eu/growth/sectors/cosmetics/cosing_en
FEMA. (2023). Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association – GRAS List. Retrieved from https://www.femaflavor.org
IFRA. (2023). IFRA Standards – 51st Amendment. International Fragrance Association.
Opdyke, D. L. J. (1974). Monographs on fragrance raw materials. Food and Cosmetics Toxicology, 12(Suppl), 653–676.
Sell, C. (2006). The Chemistry of Fragrances: From Perfumer to Consumer (2nd ed.). Royal Society of Chemistry.
Surburg, H., & Panten, J. (2016). Common Fragrance and Flavor Materials: Preparation, Properties and Uses (6th ed.). Wiley-VCH.